Image Retrieval for Image-Based Localization Revisited
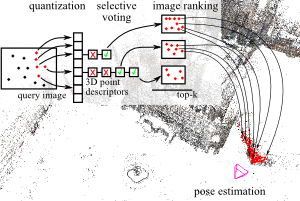
To reliably determine the camera pose of an image relative to a 3D point cloud of a scene, correspondences between 2D features and 3D points are needed. Recent work has demonstrated that directly matching the features against the points outperforms methods that take an intermediate image retrieval step in terms of the number of images that can be localized successfully. Yet, direct matching is inherently less scalable than retrieval-based approaches. In this paper, we therefore analyze the algorithmic factors that cause the performance gap and identify false positive votes as the main source of the gap. Based on a detailed experimental evaluation, we show that retrieval methods using a selective voting scheme are able to outperform state-of-the-art direct matching methods. We explore how both selective voting and correspondence computation can be accelerated by using a Hamming embedding of feature descriptors. Furthermore, we introduce a new dataset with challenging query images for the evaluation of image-based localization.

