Publications
Using Subdivision on Hierarchical Data to Reconstruct Radiosity Distribution
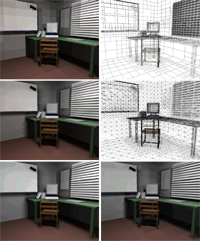
Computing global illumination by finite element techniques usually generates a piecewise constant approximation of the radiosity distribution on surfaces. Directly displaying such scenes generates artefacts due to discretization errors.We propose to remedy this drawback by considering the piecewise constant output to be samples of a (piecewise) smooth function in object space and reconstruct this function by applying a binary subdivision scheme. We design custom taylored subdivision schemes with quadratic precision for the efficient refinement of cell- or pixeltype data. The technique naturally allows to reconstruct functions from non-uniform samples which result from adaptive binary splitting of the original domain (quadtree). This type of output is produced, e.g., by hierarchical radiosity algorithms. The result of the subdivision process can be mapped as a texture on the respective surface patch which allows to exploit graphics hardware for considerably accelerating the display.
Iterative Mesh Generation for FE-Computations on Free Form Surfaces
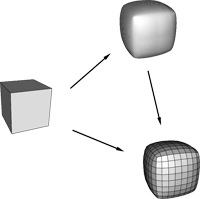
We present an interpolatory subdivision scheme to generate adaptiely refined quadrilateral meshes which approximate a smooth surface of arbitrary topology. The described method significantly differs from classical mesh generation techniques based on spline surfaces or implicit representations since no explicit description of the limit surface is used. Instead, simple affine combinations are applied to compute new vertices if a face of the net is split. These rules are designed to guarantee asymptotic smoothness, i.e., the sequence of refined nets converges to a smooth limit surface. Subdivision techniques are useful mainly in applications where a given quadrilateral net is a coarse approximation of a surface and points on a refined grid have to be estimated. To evaluate our approach, we show examples for FE-computations on surfaces generated by this algorithm.
Stable Evaluation of Box-Splines
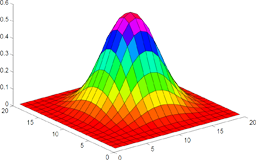
The most elegant way to evaluate box-splines is by using their recursive definition. However, a straightforward implementation reveals numerical difficulties. A careful analysis of the algorithm allows a reformulation which overcomes these problems without losing efficiency. A concise vectorized MATLAB-implementation is given.
Discrete Fairing
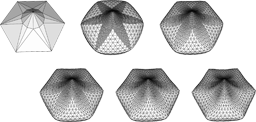
We address the general problem of, given a triangular net of arbitrary topology in IR3 , nd a re ned net which contains the original vertices and yields an improved approximation of a smooth and fair interpolating surface. The (topological) mesh re nement is performed by uniform subdivision of the original triangles while the (geometric) position of the newly inserted vertices is determined by variational methods, i.e., by the minimization of a functional measuring a discrete approximation of bending energy. The major problem in this approach is to nd an appropriate parameterization for the re ned net's vertices such that second divided di erences (derivatives) tightly approximate intrinsic curvatures. We prove the existence of a unique optimal solution for the minimization of discrete functionals that involve squared second order derivatives. Finally, we address the e cient computation of fair nets.
Robust and Efficient Evaluation of Functionals on Parametric Surfaces
Previous Year (1996)

