Profile

|
Publications
Near-Constant Density Wireframe Meshes for 3D Printing
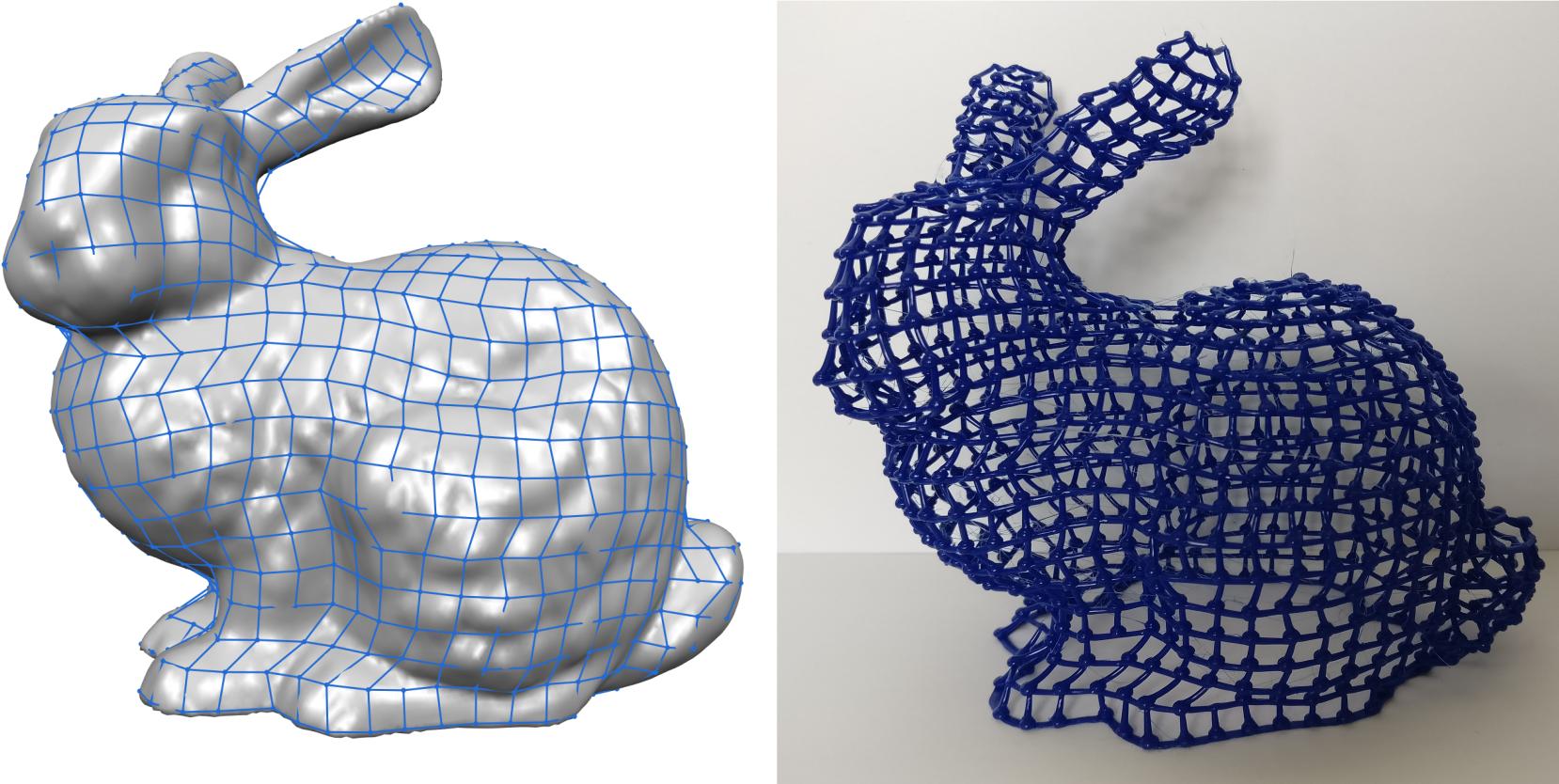
In fused deposition modeling (FDM) an object is usually constructed layer-by-layer. Using FDM 3D printers it is however also possible to extrude filament directly in 3D space. Using this technique, a wireframe version of an object can be created by directly printing the wireframe edges into 3D space. This way the print time can be reduced and significant material saving can be achieved. This paper presents a technique for wireframe mesh generation with application in 3D printing. The proposed technique transforms triangle meshes into polygonal meshes, from which the edges can be printed to create the wiremesh. Furthermore, the method is able to generate near-constant density of lines, even in regions parallel to the build platform.
Scalable 6-DOF Localization on Mobile Devices
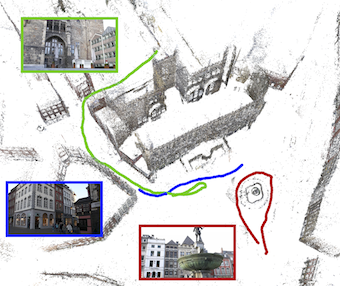
Recent improvements in image-based localization have produced powerful methods that scale up to the massive 3D models emerging from modern Structure-from-Motion techniques. However, these approaches are too resource intensive to run in real-time, let alone to be implemented on mobile devices. In this paper, we propose to combine the scalability of such a global localization system running on a server with the speed and precision of a local pose tracker on a mobile device. Our approach is both scalable and drift-free by design and eliminates the need for loop closure. We propose two strategies to combine the information provided by local tracking and global localization. We evaluate our system on a large-scale dataset of the historic inner city of Aachen where it achieves interactive framerates at a localization error of less than 50cm while using less than 5MB of memory on the mobile device.
The final publication will be available at link.springer.com upon publication.
@inproceedings{middelberg2014eccv,
author = "Middelberg, Sven and Sattler, Torsten and Untzelmann, Ole and Kobbelt, Leif",
title = "{Scalable 6-DOF Localization on Mobile Devices}",
booktitle = "{Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV'14)}",
year = 2014
}
A Scalable Collaborative Online System for City Reconstruction

Recent advances in Structure-from-Motion and Bundle Adjustment allow us to efficiently reconstruct large 3D scenes from millions of images. However, acquiring the imagery necessary to reconstruct a whole city and not only its landmark buildings still poses a tremendous problem. In this paper, we therefore present an online system for collaborative city reconstruction that is based on crowdsourcing the image acquisition. Employing publicly available building footprints to reconstruct individual blocks rather than the whole city at once enables our system to easily scale to large urban environments. In order to map all partial reconstructions into a single coordinate frame, we develop a robust alignment scheme that registers the individual point clouds to their corresponding footprints based on GPS coordinates. Our approach can handle noise and outliers in the GPS positions and allows us to detect wrong alignments caused by the typical issues in the context of crowdsourcing applications such as malicious or improper image uploads. Furthermore, we present an efficient rendering method to obtain dense and textured views of the resulting point clouds without requiring costly multi-view stereo methods
@inproceedings{untzelmann2013iccv,
author = "Untzelmann, Ole and Sattler, Torsten and Middelberg, Sven and Kobbelt, Leif",
title = "{A Scalable Collaborative Online System for City Reconstruction}",
booktitle = "{The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops}",
year = {2013}
}

